对许多将英语作为第二语言来学习的人来说,时态是一个令人困惑的话题。在下面的信息中,我尽量用简单的语言回答“什么是时态?”、“我如何改变动词的时态?”、“我该在什么时候使用动词的不同时态?”以及“为什么需要使用某个特定的时态?”,并指出其中的要点。
这些信息的描述并不穷尽,但是可以作为指南帮助你理解基本知识。
什么是时态?怎样使用时态?
下面是一些拆分后的句子成分,解释了英语中什么是时态,以及怎么根据时态改变动词的形态。
一般时
Subject + Verb (past form)
例如: I jumped 或 He taught
进行时
Subject + to be (verb, past form) + verb + ing
例如: I was jumping 或 He was teaching
完成时
Subject + to have(verb,
past form) + Verb (past participle)
例如: I had jumped 或 He had taught
一般时
Subject + verb
Example: I jump or He teaches
进行时
Subject + to be(verb) + verb + ing
Example: I am jumping or He is teaching
完成时
Subject + to have(verb) + Verb (past participle)
Example: I have jumped or He has taught
一般时
Subject + will + verb
Example: I will jump or He will jump
进行时
Subject + will + be + verb + ing
Example: I will be jumping or He will be teaching
完成时
Subject + will + have + Verb (past participle)
Example: I will have jumped or He will have taught
什么时候需要改变时态?为什么要改变时态?
一般时
- Describes something that happened in the past that is finished. – I went to Heihe for Chinese New Year
进行时
- Describe actions that weren’t finished that happened over a period of time in the past. – Last month, I was trying to get a new job.
- Describe actions that were changing in the past – Last year, the world was still coming out of recession.
完成时
- Describes something that started in the past, refers further back to the past and then continues up to the first point in the past – In 2010, I have lived in China for five years.
一般时
- Describes predictions – It will be a nice day tomorrow
- Describes the desire or willingness to do something – George says he will help us
进行时
- Describes plans and intentions – I will be driving to work today
- to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future – I will be waiting for you when your bus arrives
完成时
- Expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
“to be”和“to have”的时态变化
| To be – (现在时) | To be (过去时) | ||||||
| 单数 | 复数 | 单数 | 复数 | ||||
1st 人称 | I | am | We | are | I | was | We | were |
2nd 人称 | You | are | You | are | You | were | You | were |
3rd 人称 | He/she/it | is | They | are | He/she/it | were | They | were |
| To have – (现在时) | To have (过去时) | ||||||
| 单数 | 复数 | 单数 | 复数 | ||||
1st 人称 | I | have | We | have | I | had | We | had |
2nd 人称 | You | have | You | have | You | had | You | had |
3rd 人称 | He/she/it | has | They | have | He/she/it | had | They | had |
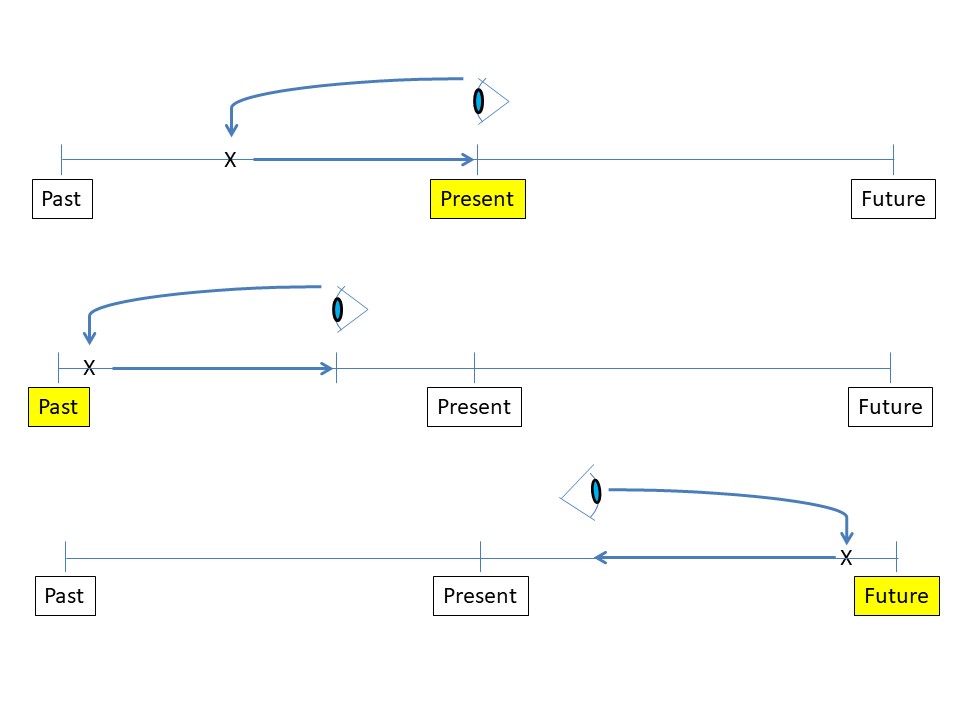
时态的时间线
一般时
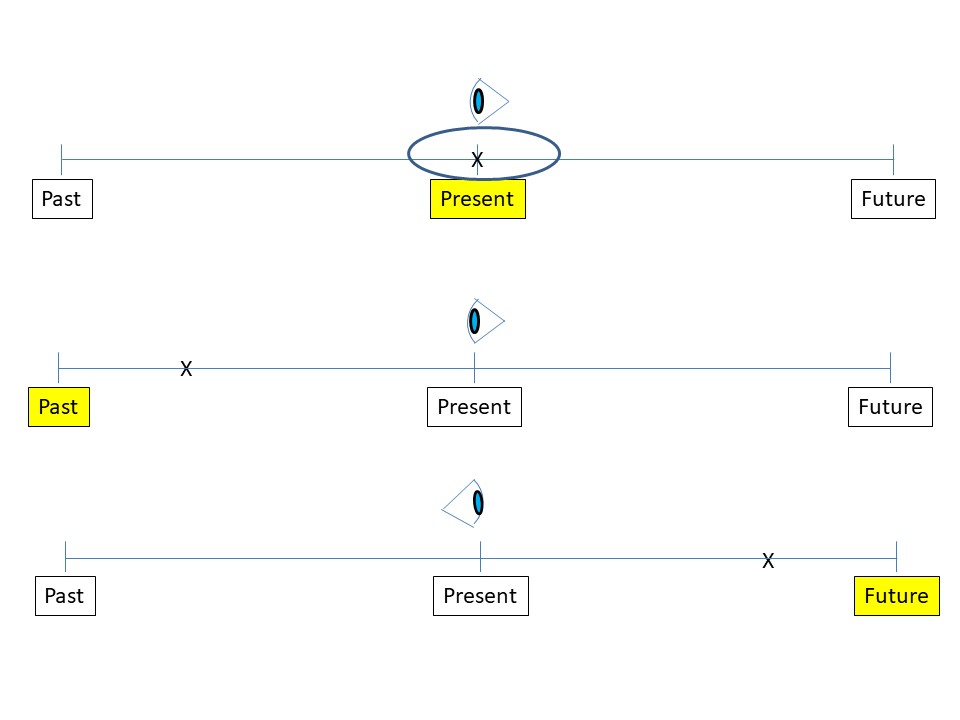
进行时
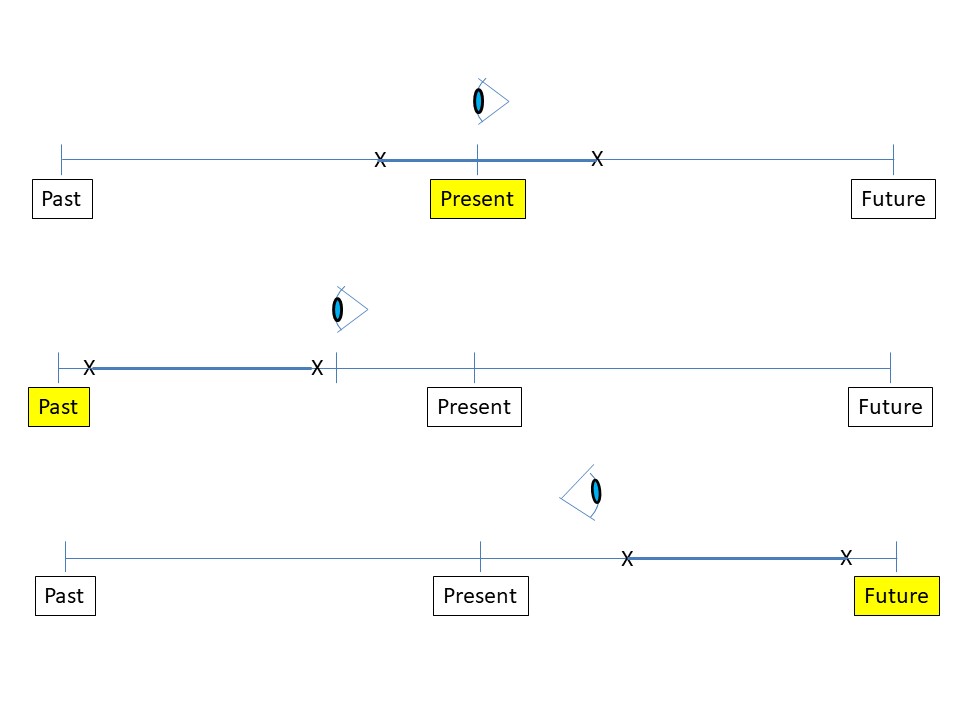
完成时