For many people learning English as a second language, tenses are a confusing topic. In the following information, I have tried simplifying some of the main points you need to know when asking, “What are Tenses?”, “How do I change (or conjugate) the verbs?” as well as the “When should I use them?” and “Why use that particular tense?” I’ve also included a breakdown of the verbs to be and have and some visual timelines that may help you understand everything more.
It is by no means an exhaustive description but merely a small guide to help you understand the basics.
The What/How of Tenses
Below is a simple breakdown of ‘What’ the tenses are in English and ‘How’ to change the verb structure.
Simple
Subject + Verb (past form)
Example: I jumped or He taught
Continuous
Subject + to be (verb, past form) + verb + ing
Example: I was jumping or He was teaching
Perfect
Subject + to have(verb,
past form) + Verb (past participle)
Example: I had jumped or He had taught
Simple
Subject + verb
Example: I jump or He teaches
Continuous
Subject + to be(verb) + verb + ing
Example: I am jumping or He is teaching
Perfect
Subject + to have(verb) + Verb (past participle)
Example: I have jumped or He has taught
Simple
Subject + will + verb
Example: I will jump or He will jump
Continuous
Subject + will + be + verb + ing
Example: I will be jumping or He will be teaching
Perfect
Subject + will + have + Verb (past participle)
Example: I will have jumped or He will have taught
The When/Why of tenses
Simple
- Describes something that happened in the past that is finished. – I went to Heihe for Chinese New Year
Continuous
- Describe actions that weren’t finished that happened over a period of time in the past. – Last month, I was trying to get a new job.
- Describe actions that were changing in the past – Last year, the world was still coming out of recession.
Perfect
- Describes something that started in the past, refers further back to the past and then continues up to the first point in the past – In 2010, I have lived in China for five years.
Simple
- Describes predictions – It will be a nice day tomorrow
- Describes the desire or willingness to do something – George says he will help us
Continuous
- Describes plans and intentions – I will be driving to work today
- to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future – I will be waiting for you when your bus arrives
Perfect
- Expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
The details of the verbs 'to be' and 'to have'
| To be – (present) | To be (past) | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||||
1st person | I | am | We | are | I | was | We | were |
2nd person | You | are | You | are | You | were | You | were |
3rd person | He/she/it | is | They | are | He/she/it | were | They | were |
| To have – (present) | To have (past) | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||||
1st person | I | have | We | have | I | had | We | had |
2nd person | You | have | You | have | You | had | You | had |
3rd person | He/she/it | has | They | have | He/she/it | had | They | had |
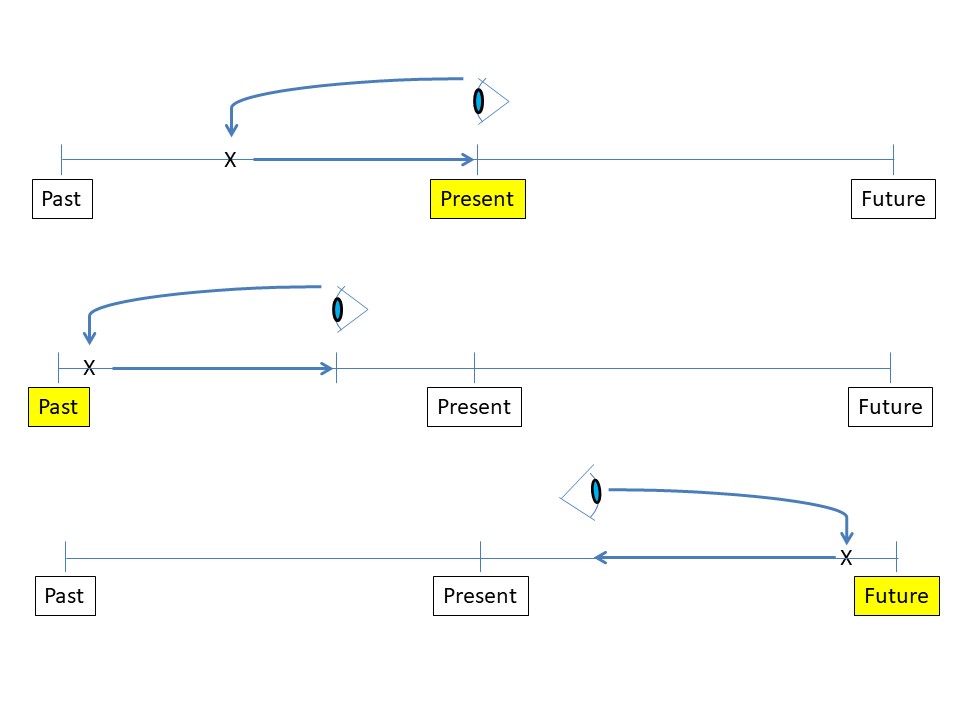
Tense Timelines
Simple
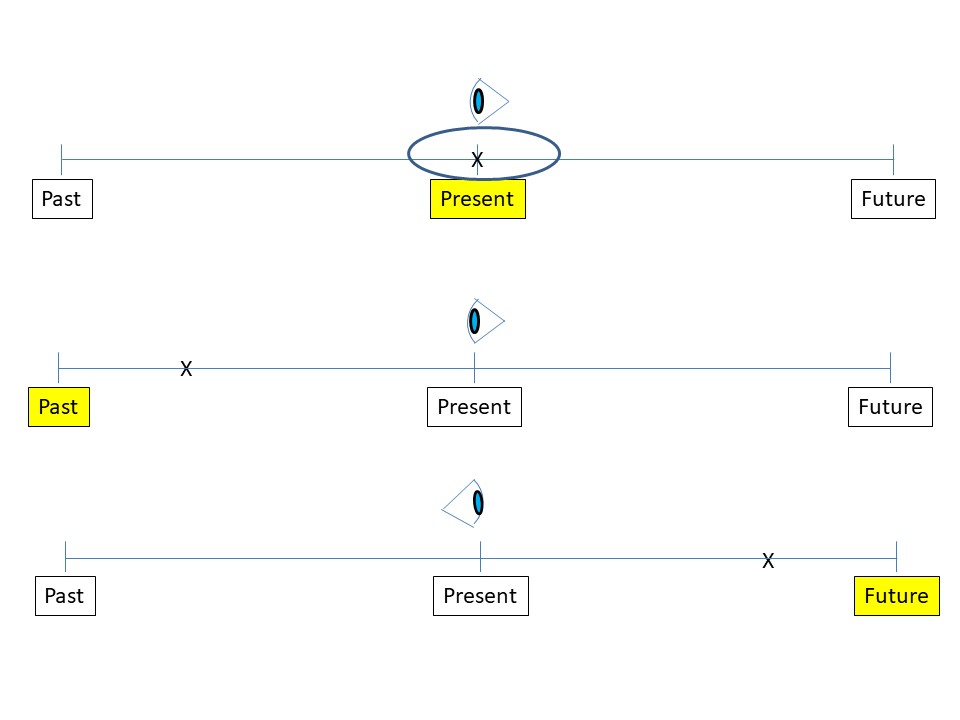
Continuous
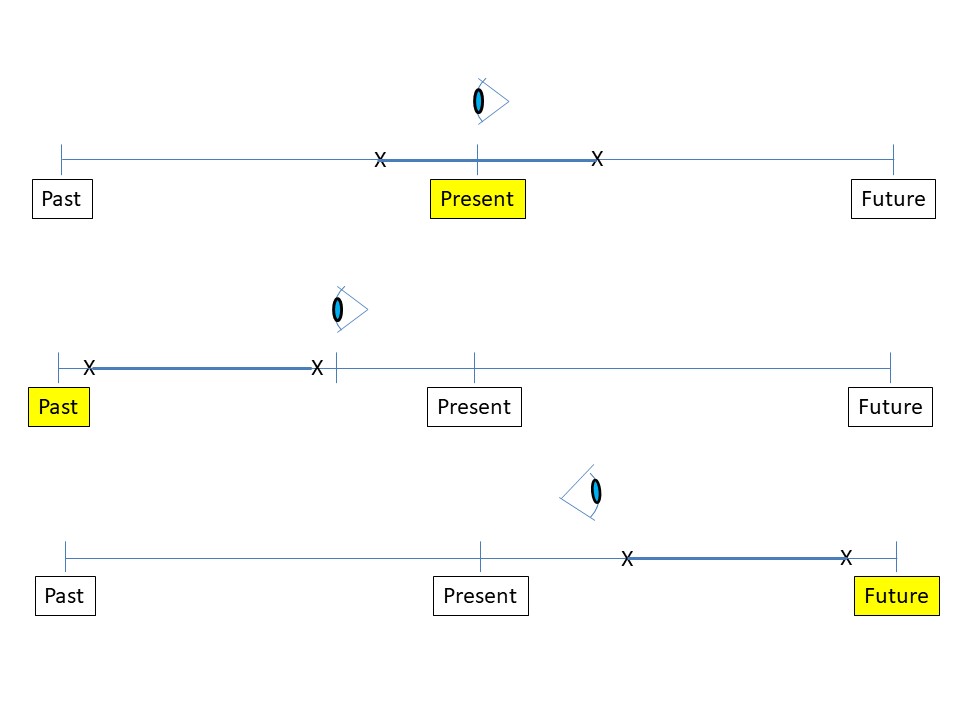
Perfect